Key Takeaways
- As the energy sector shifts to renewables, global power dynamics are evolving, supported by policies and infrastructure upgrades that drive decarbonization.
- EV development and charging innovations are pushing the automotive and technology industries toward greater renewable energy adoption.
- To meet growing green demands and stricter environmental regulations, the construction industry is prioritizing energy-efficient buildings and renewable infrastructure.
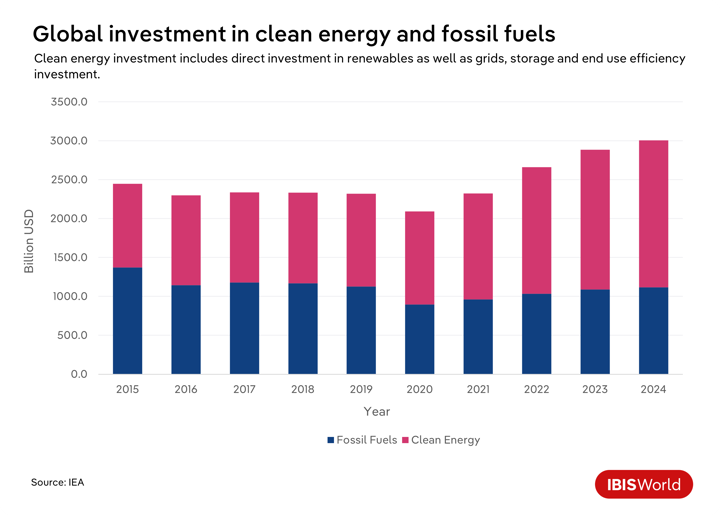
The rise of renewables is powering more than grids; it’s powering economic transformation. Global investment in clean energy technologies and infrastructure reached $2 trillion USD in 2024, nearly double the spending on fossil fuels.
Investment in renewable energy has accelerated in recent years, most recently bolstered by COP28 when over 145 countries agreed to work together to triple the world’s installed renewable energy capacity by 2030. Soaring oil and natural gas prices in the first half of 2022, owing to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, also bolstered renewable energy investment as an alternative to fossil fuels. Since then, spending on renewable power, grids and storage has surpassed total spending on oil, gas and coal.
Spearheaded by governmental policies, ambitious sustainability targets, and the consumer pivot towards eco-conscious brands, the thrust towards green energy is reshaping entire industry landscapes. Global renewable electricity use in the transport, manufacturing and construction sectors accounted for approximately three-quarters of renewable energy demand in 2023, and these three sectors alone are set to boost the share of renewables in final energy consumption to nearly 20% by 2030, up from 13% in 2023. Understanding which sectors are at the forefront of this shift not only reveals the strategic adjustments industries are making but also illuminates the pathways for potential investors and companies wishing to align with future market trajectories.
How green capital is redefining the energy sector
The energy sector is rapidly investing in renewables to decarbonize power generation and meet net-zero targets. Volatile oil and gas prices from geopolitical tensions in Europe and the Middle East have also driven governments to prioritize energy security. In 2023-24, renewables accounted for 30% of global power generation, a figure projected to grow to 46% by 2030, with solar and wind leading this expansion.
This growth spills into other sectors, helping decarbonize industrial processes, heating, and EV charging. Within energy, heavy investments are needed to boost generation, storage, and transmission, impacting providers in heating and utilities. Renewable electricity is forecast to account for over three-quarters of the rise in energy consumption by 2030, supported by policies in 130+ countries, falling costs, and expanding electricity applications. Renewable heating is also set to grow by over 50%, driven by electricity use in industries and buildings.

Globally, renewable energy is reshaping power production, with the US, UK, and Australia leading the shift. In the US, renewables make up 22% of power generation, below the global average. However, solar farms, offshore wind, and tax credits—making up 99% of utility-scale renewable investments—are driving growth. Federal policies, such as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Act, are funding critical grid upgrades, including new transmission lines. Programs like the Transition Facilitation Program are expanding grid capacity, spurring renewable growth in states like Texas, Maine, and California, the largest US renewable market.

In the UK, renewables account for 48% of power generation, well above the global average. Government initiatives, like the Clean Power 2030 Action Plan, aim for 100% clean electricity by 2030, with offshore wind playing a key role. The UK, a leader in offshore wind, has 14.8 gigawatts of capacity and plans to reach 50 gigawatts by 2030. Initiatives like the Green Financing Framework and Net Zero Innovation Portfolio are driving billions in funding for renewable projects, including emerging technologies like tidal energy.
Australia is also making progress, with solar and wind providing 34% of energy, slightly above the global average. Companies like AGL Energy are leveraging federal and state programs, such as the Capacity Investment Scheme, to expand solar and wind projects. Advances in battery storage are improving grid reliability, while solar PV capacity is set to grow by nearly 14 gigawatts by 2030. Australia is also phasing out coal, with all coal-fired plants expected to close by 2038, accelerating green energy investments.
Across these regions, the transition to clean energy is marked by ambitious goals, major investments, and technological advancements. While challenges vary, the shared focus remains on expanding renewable capacity and modernizing infrastructure to meet energy demands sustainably. With strong policies and innovation, the renewable energy sector is set for continued growth and transformation.
Strategies for identifying opportunities in green energy investment
- Leverage data on industry trends and five-year projections to identify high-growth renewable energy markets and emerging opportunities.
- Use geographic breakdowns and competitor analysis to pinpoint untapped regions and avoid market saturation in green energy investments.
- Evaluate emerging technologies and their commercial readiness to assess the viability of investing in next-gen energy solutions like hydrogen and carbon capture.
- Monitor regulatory changes, industry disruptions, and supply chain dynamics to anticipate shifts in the green energy sector and adjust investment strategies accordingly.
Green energy drives manufacturing innovation
Manufacturing, at the heart of supply chains and operational efficiency, is steadily embracing renewable energy to enhance sustainability and reduce costs. This shift is particularly evident in sectors like wind turbines and solar panels, which are experiencing rapid growth and signaling a broader move toward greener practices.
However, the transition to renewable energy is not without its challenges. Manufacturing consumes significantly more energy than other sectors, making the switch to renewables both costly and complex. Manufacturing accounts for 20% of global energy use, a figure that continues to rise as companies adopt electrified production methods. Despite these hurdles, industries around the world are finding innovative ways to lead this transformation.

In the U.S., industries like automotive and tech are paving the way. Automakers are not only producing electric vehicles but are also integrating renewable energy into their manufacturing processes. For example, General Motors has secured a 15-year solar energy deal for its plants, aiming for 100% renewable energy by 2035, an effort supported by tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act. Meanwhile, aerospace giant Boeing is addressing the aviation sector's carbon footprint with sustainable fuels, targeting net-zero emissions by 2050.
This shift extends beyond end-user industries and into the production of renewable energy technologies themselves. The manufacturing of wind turbines and solar panels is undergoing a transformation, supported by tax incentives and state programs. While the International Energy Agency predicts potential delays in wind turbine production by 2030 due to supply chain and grid challenges, steady demand for solar panels is expected to offset such setbacks, keeping the renewables sector on track.
In the UK, similar progress is evident. Automotive and aerospace industries are heavily investing in electric vehicles (EVs), energy-efficient engines, and complementary sectors like battery and charger production. In 2023-24, 35.5% of renewable energy investments (£4.1 billion) were directed toward EV initiatives such as the Electric Vehicle Homecharge Scheme. Private investments have also been significant, with over £23.5 billion allocated to new EV models. Companies like Rolls-Royce have joined the effort, advancing renewable fuel facilities and energy-efficient engines to achieve net-zero goals.

Australia is also making strides in renewable energy adoption within manufacturing. Manufacturing is the country’s largest energy user, yet renewables currently account for just 10% of its consumption. The government’s $1 billion Solar Sunshot program aims to change this, driving both solar PV production and adoption. The food and beverage sector is leading by example, with Mars Wodonga in Victoria set to become the country’s first large-scale steam-based site to run entirely on renewable energy by 2026. This project, made possible by a $39 million investment in a Concentrated Solar Thermal (CST) system, highlights Australia’s potential to leverage its abundant sunlight for industry-wide transformation.
From the U.S. to the UK and Australia, the shift to renewable energy in manufacturing is becoming a global phenomenon. While challenges remain, the momentum is undeniable. By embracing green energy, manufacturers are not only cutting costs but also laying the groundwork for a more sustainable future.
Strategies for unlocking opportunities in renewable energy for manufacturing
- Leverage government incentives and tax credits to identify which manufacturing sectors are accelerating their transition to renewable energy and driving growth.
- Focus on industries with high energy consumption, like automotive and aerospace, to uncover opportunities in the integration of renewable energy and energy-efficient technologies.
- Track regional initiatives and large-scale projects (e.g., solar programs in Australia) to understand where renewable energy adoption is most impactful within manufacturing.
- Assess the long-term viability of renewable energy investments in manufacturing by monitoring government-led initiatives, such as solar and electric vehicle programs, and private sector innovation.
How green power is reinventing construction practices
The construction industry is undergoing a global transformation, driven by the growing demand for infrastructure that supports renewable energy production, storage, and efficient use. This shift is fueling investments in areas such as household solar panel installation and EV charging infrastructure, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Sustainable buildings are also gaining traction, as businesses and consumers increasingly seek energy-efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly solutions. Companies that deliver green construction projects stand to benefit not only from heightened demand but also from tax incentives aimed at promoting sustainability. Advances in renewable energy integration, energy storage solutions to address supply and intermittency challenges, and smart building systems are opening up new opportunities in the sector. By leveraging these technologies, construction companies can enhance efficiency, cut costs, and improve project outcomes.

In the US, the green construction movement is rapidly expanding. Developers are increasingly integrating sustainability into their projects, with contractors achieving certifiable green targets gaining access to tax credits through energy-efficient commercial building deductions. Retail stores and warehouses are leading the way, with 1.6% of warehouse projects now meeting over half of their energy needs through on-site renewable energy. Residential construction is also experiencing a green investment boom, thanks to government incentives. Contractors can claim up to $5,000 per home in tax credits for energy-efficient projects, while roofing contractors are seeing increased demand for solar panels and green roofing systems that absorb rainwater and reduce heating and cooling costs.
Across the Atlantic, the UK is heavily investing in renewable energy projects within the construction sector. In 2023-24, £720.3 million—approximately 6% of the UK government’s Green Financing Program—was allocated to improving building energy efficiency and supporting the energy transition. While on-site renewable energy generation is less common in the UK, initiatives like heat networks, energy efficiency upgrades, and programs such as the Green Homes Grant are driving advancements in residential and commercial construction. Clean transportation investment is further boosting the construction industry. In the UK, £115.5 million, or 2.8% of clean transportation funding, is reserved for EV charging infrastructure to support the growing adoption of electric vehicles.

Looking to Australia, the construction industry is adapting to meet stricter environmental standards, particularly in commercial and infrastructure projects. Photovoltaic installations within transport infrastructure and sustainable building practices are reducing future compliance costs while aligning with the country’s renewable energy goals. Key projects, such as the Gippsland Dawn Offshore Wind Project, are creating jobs and generating clean power, with Gippsland Dawn alone projected to supply electricity to one million homes. The rise of EVs is also a game changer for Australian construction. Government funding, such as the Driving the Nation Fund, has allocated $39.3 million to install 117 EV chargers along major highways, while Victoria is investing $19 million to expand statewide charging infrastructure in 2024.
The construction sector is at the center of the global push for renewable energy and sustainable practices. As investments grow and technologies advance, construction companies that embrace these changes are well-positioned to thrive in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Final Word
As we scrutinize the green energy narrative, it's clear that investment in renewables is both a strategic necessity and an economic opportunity across leading sectors. The energy, manufacturing and construction sectors are spearheading this transition, leveraging policy incentives, tax benefits, technological advancements and strategic infrastructure developments to future-proof their operations.
For companies to best prepare for the future, they must embed renewable strategies at the core of their operational planning, leveraging industry-level analysis and benchmarking. R&D will also remain a focal point of green investment, driving innovation in energy-efficient technologies and processes for companies that take advantage of policy incentives. By harnessing this vision, industries not only position themselves at the forefront of technological advancement but also secure their footprint in a sustainable and profitable future. As the global discourse increasingly favors sustainable practices, how businesses adapt today could very well define the economic landscapes of tomorrow.